The Remote Work Security Revolution: Protecting Your Distributed Workforce in 2025
The statistics are staggering: 73% of security breaches now involve remote work vulnerabilities. What began as an emergency pandemic response has evolved into a permanent transformation of how we work, fundamentally reshaping the cybersecurity landscape. Organizations that treated remote work as a temporary accommodation are now grappling with the reality that distributed workforces are here to stay—and so are the sophisticated threats targeting them.
The traditional security perimeter has dissolved. Employees work from home offices, coffee shops, coworking spaces, and while traveling. They access corporate resources through personal devices, home networks, and public Wi-Fi connections. This new reality demands a complete reimagining of enterprise cybersecurity strategies.
The New Remote Work Threat Landscape
Beyond the Home Office: The Expanding Attack Surface
Remote work has created an unprecedented expansion of organizational attack surfaces. Consider the complexity:
Geographic Distribution: Employees span multiple time zones, countries, and regulatory jurisdictions, each with unique security challenges and compliance requirements.
Device Diversity: The bring-your-own-device (BYOD) trend has accelerated, with employees using personal laptops, tablets, smartphones, and IoT devices to access corporate resources.
Network Variability: Corporate data flows through home broadband connections, public Wi-Fi networks, cellular hotspots, and shared coworking spaces—many lacking enterprise-grade security controls.
Physical Security Challenges: Sensitive information is accessed and stored in environments with varying levels of physical security, from secure home offices to bustling coffee shops.
Sophisticated Threat Actors Adapting
Cybercriminals have rapidly adapted their tactics to exploit remote work vulnerabilities:
Home Network Infiltration: Attackers target poorly secured home routers and IoT devices to gain persistent access to corporate networks.
COVID-Themed Social Engineering: Threat actors leverage pandemic-related anxieties, vaccine information, and remote work policies to craft convincing phishing campaigns.
Supply Chain Attacks Through Remote Access: Cybercriminals infiltrate organizations by compromising remote access tools, collaboration platforms, and cloud services.
Ransomware Targeting Remote Infrastructure: Criminal organizations specifically target remote desktop protocols (RDP) and VPN vulnerabilities to deploy ransomware.
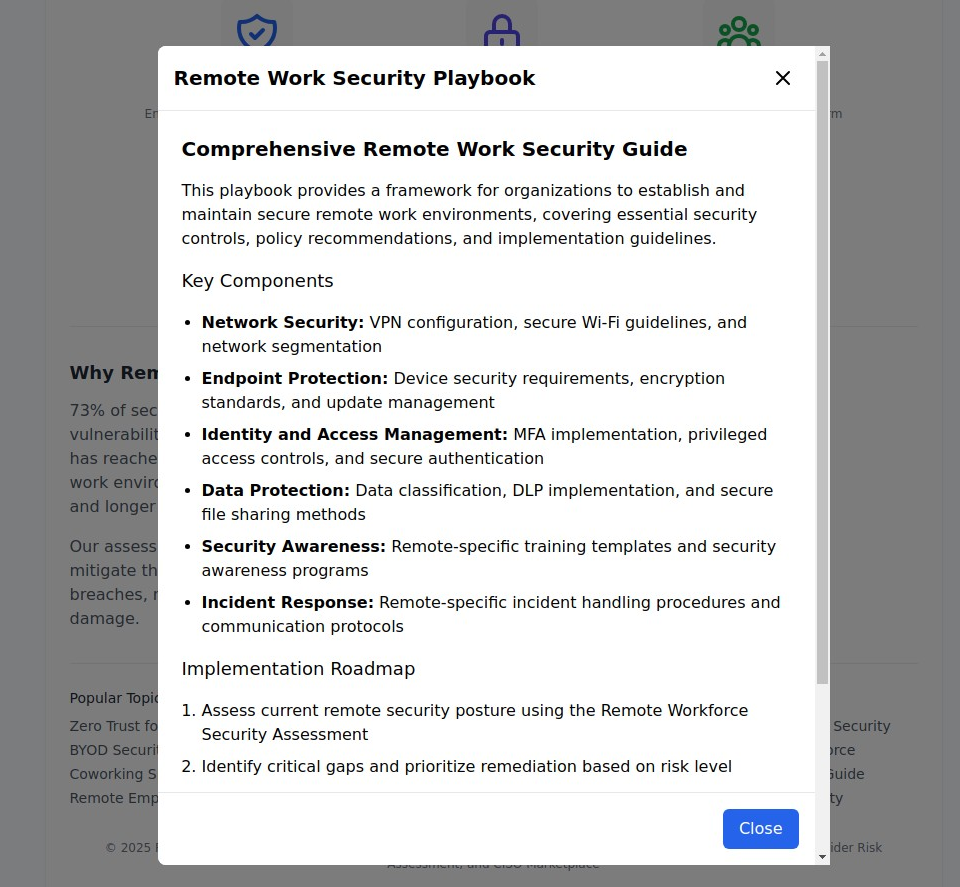
The Six Pillars of Remote Work Security Excellence
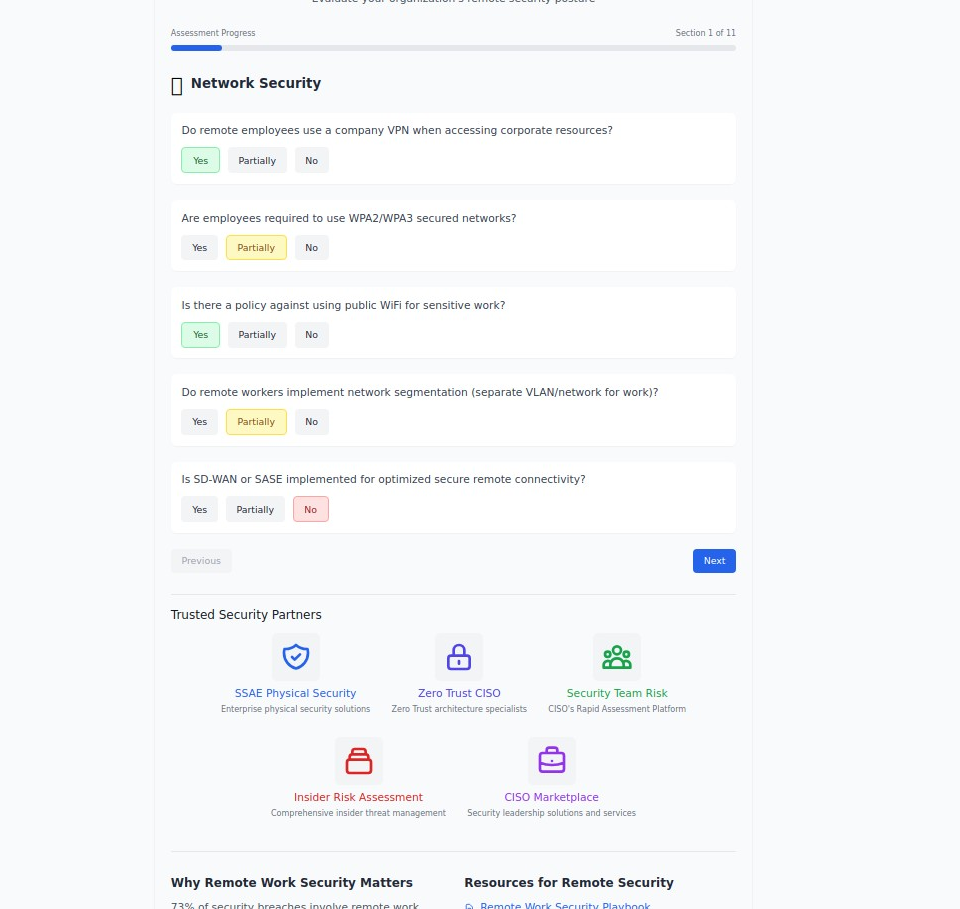
1. Network Security: Building Secure Digital Highways
Modern remote work demands sophisticated network security architectures that protect data in transit across untrusted networks.
VPN Strategy Evolution Traditional VPNs, while essential, are no longer sufficient. Organizations must implement:
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Verify every connection attempt regardless of location
- Software-Defined Perimeters: Create secure, encrypted tunnels for specific applications
- Cloud-Native VPN Solutions: Leverage cloud infrastructure for scalable, reliable remote access
Secure Connectivity Standards
- WPA3 Enforcement: Require the latest Wi-Fi security standards for all remote connections
- Public Wi-Fi Policies: Establish clear guidelines prohibiting sensitive work on unsecured networks
- Network Segmentation: Implement micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement in case of compromise
SD-WAN and SASE Implementation
- Software-Defined Wide Area Networks: Optimize and secure traffic routing for remote locations
- Secure Access Service Edge: Combine network security and WAN capabilities in unified cloud platforms
- Performance Optimization: Ensure security measures don't compromise user experience or productivity
2. Endpoint Protection: Securing Every Device
With corporate data accessed from countless devices in uncontrolled environments, endpoint protection becomes critical.
Device Security Requirements
- Full Disk Encryption: Protect data at rest on all devices accessing corporate resources
- Automatic Updates: Ensure operating systems and applications receive timely security patches
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Deploy advanced threat detection on all corporate-managed devices
Mobile Device Management (MDM)
- Application Control: Restrict installation of unauthorized applications that could introduce vulnerabilities
- Data Loss Prevention: Prevent sensitive information from being copied to unsecured locations
- Remote Wipe Capabilities: Enable secure data removal from lost or compromised devices
Personal Device Considerations
- Containerization: Separate corporate and personal data on employee-owned devices
- Compliance Monitoring: Verify that personal devices meet minimum security standards
- Privacy Protection: Balance security requirements with employee privacy expectations
3. Identity and Access Management: Verifying Every User
Remote work environments require robust identity verification and access controls that function seamlessly across diverse environments.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Universal MFA Deployment: Require additional authentication factors for all system access
- Adaptive Authentication: Adjust security requirements based on risk factors like location and device
- Passwordless Solutions: Implement biometric and hardware-based authentication methods
Privileged Access Management
- Just-in-Time Access: Provide elevated privileges only when needed for specific tasks
- Privileged Session Monitoring: Record and analyze all administrative activities
- Emergency Access Procedures: Maintain secure processes for urgent system access needs
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration
- Centralized Authentication: Reduce password fatigue while maintaining security through unified login systems
- Application Integration: Ensure all corporate applications support modern authentication standards
- Session Management: Implement intelligent session timeouts and re-authentication requirements
4. Data Protection: Safeguarding Information Everywhere
With sensitive data accessed from countless locations and devices, comprehensive data protection strategies are essential.
Data Classification and Handling
- Automated Classification: Use artificial intelligence to identify and tag sensitive information
- Handling Policies: Establish clear guidelines for different data sensitivity levels
- Retention Management: Implement automated policies for data lifecycle management
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Endpoint DLP: Monitor and control data movement from individual devices
- Cloud DLP: Protect information stored and processed in cloud applications
- Email Security: Scan outbound communications for sensitive information leakage
Secure File Sharing
- Encrypted Collaboration Platforms: Use secure alternatives to consumer file-sharing services
- Access Controls: Implement granular permissions for shared documents and folders
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs of all file access and modification activities
5. Security Awareness: Building Human Firewalls
Remote workers face unique security challenges that require specialized training and awareness programs.
Remote-Specific Training
- Home Office Security: Educate employees about securing their physical workspace
- Public Wi-Fi Risks: Provide clear guidance about safe practices in public spaces
- Social Engineering Recognition: Train employees to identify remote work-targeted attacks
Ongoing Awareness Programs
- Simulated Phishing: Conduct regular testing using remote work themes and scenarios
- Security Updates: Keep employees informed about emerging threats and protective measures
- Incident Reporting: Establish clear, accessible channels for reporting security concerns
Cultural Integration
- Security Champions: Identify and train remote employees to serve as local security advocates
- Regular Communication: Maintain consistent security messaging through multiple channels
- Recognition Programs: Reward employees who demonstrate excellent security practices
6. Incident Response: Rapid Response in Distributed Environments
Remote work incidents present unique challenges that require specialized response procedures.
Remote-Specific Response Plans
- Isolation Procedures: Develop methods for quarantining compromised remote devices
- Communication Protocols: Establish reliable channels for coordinating incident response
- Evidence Collection: Create procedures for gathering forensic evidence from remote locations
Distributed Response Teams
- Regional Coordinators: Designate incident response leaders in key geographic areas
- Remote Investigation Tools: Deploy capabilities for analyzing incidents without physical access
- Third-Party Coordination: Establish relationships with local incident response providers
Business Continuity Planning
- Alternative Work Arrangements: Prepare backup plans for continued operations during incidents
- Communication Continuity: Ensure multiple channels remain available during security events
- Recovery Procedures: Develop streamlined processes for restoring remote work capabilities
Industry-Specific Remote Work Challenges
Healthcare: HIPAA Compliance in Home Offices
Healthcare organizations face unique challenges protecting patient information in remote environments:
Telehealth Security
- Platform Compliance: Ensure video conferencing and communication tools meet HIPAA requirements
- Patient Data Protection: Implement controls preventing unauthorized access to medical records
- Device Management: Secure personal devices used for patient care activities
Home Office PHI Protection
- Physical Safeguards: Establish requirements for securing printed patient information
- Family Member Access: Prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing patient data
- Disposal Procedures: Create secure methods for destroying sensitive information
Financial Services: PCI DSS in Distributed Environments
Financial institutions must maintain payment card security across remote work environments:
Remote Payment Processing
- Secure Environments: Establish requirements for accessing cardholder data from home
- Network Segmentation: Isolate payment processing systems from home network traffic
- Audit Compliance: Maintain PCI DSS compliance across distributed work locations
Customer Data Protection
- Secure Communications: Encrypt all channels used for transmitting financial information
- Access Monitoring: Implement comprehensive logging for all customer data access
- Fraud Prevention: Deploy advanced analytics to detect suspicious remote access patterns
Technology: Intellectual Property Protection
Technology companies must protect valuable intellectual property accessed by remote employees:
Source Code Security
- Repository Access: Implement secure methods for accessing development environments
- Code Review Processes: Maintain security review standards for remote development
- Backup and Recovery: Ensure secure backup of critical development assets
Trade Secret Protection
- Confidentiality Agreements: Update legal frameworks for remote work environments
- Data Compartmentalization: Limit access to sensitive projects based on need-to-know principles
- Monitoring Systems: Deploy tools to detect unauthorized access to proprietary information
Coworking and Shared Spaces: Special Considerations
The rise of coworking spaces and shared offices creates unique security challenges:
Physical Security Measures
Workspace Selection
- Security Assessment: Evaluate physical security measures of coworking facilities
- Access Controls: Understand who has access to shared spaces and work areas
- Surveillance Systems: Verify presence of security cameras and monitoring systems
Information Protection
- Screen Privacy: Use privacy filters to prevent shoulder surfing
- Document Security: Avoid printing sensitive information in shared environments
- Clean Desk Policies: Ensure no sensitive information is left unattended
Network Security in Shared Spaces
Wi-Fi Security
- Network Evaluation: Assess security of coworking space wireless networks
- VPN Requirements: Mandate VPN use for all corporate access from shared networks
- Traffic Monitoring: Be aware that network activity may be visible to other users
Isolation Techniques
- Personal Hotspots: Use cellular connections for sensitive work when possible
- Network Segmentation: Implement client isolation to prevent lateral access
- Encrypted Communications: Ensure all sensitive communications use end-to-end encryption
Emerging Technologies and Future Considerations
Zero Trust Architecture Implementation
The future of remote work security lies in Zero Trust principles:
Identity-Centric Security
- Continuous Verification: Authenticate and authorize every access attempt
- Risk-Based Decisions: Adjust security requirements based on real-time risk assessment
- Micro-Segmentation: Limit access to specific resources rather than entire networks
Technology Integration
- Cloud-Native Solutions: Leverage cloud infrastructure for scalable Zero Trust implementation
- AI-Powered Analytics: Use machine learning to detect anomalous behavior patterns
- Automated Response: Implement systems that can respond to threats without human intervention
Artificial Intelligence in Remote Security
AI technologies are transforming remote work security:
Behavioral Analytics
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Detect unusual patterns in remote work activities
- Anomaly Detection: Identify potential security incidents through statistical analysis
- Predictive Modeling: Anticipate and prevent security incidents before they occur
Automated Threat Response
- Intelligent Orchestration: Coordinate complex response activities across distributed environments
- Adaptive Policies: Automatically adjust security controls based on changing threat landscapes
- Decision Support: Provide security teams with AI-powered insights for incident response
Extended Reality (XR) and the Metaverse
As virtual and augmented reality technologies mature, new security challenges emerge:
Virtual Workspace Security
- Avatar Authentication: Verify identity in virtual environments
- Data Protection: Secure sensitive information shared in virtual spaces
- Platform Security: Ensure virtual reality platforms meet enterprise security standards
Privacy Considerations
- Biometric Data: Protect physiological information collected by XR devices
- Behavioral Tracking: Manage privacy implications of detailed movement and interaction monitoring
- Cross-Platform Integration: Secure data sharing between virtual and traditional work environments
Building a Remote-First Security Culture
Leadership and Governance
Successful remote work security requires committed leadership and clear governance:
Executive Sponsorship
- Security Investment: Allocate adequate resources for remote work security initiatives
- Policy Development: Establish comprehensive remote work security policies
- Performance Metrics: Define and track key security indicators for remote work
Risk Management
- Regular Assessments: Conduct periodic evaluations of remote work security posture
- Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about evolving threats targeting remote workers
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly update security measures based on lessons learned
Employee Empowerment
Successful remote work security depends on engaged, educated employees:
Security Tools Accessibility
- User-Friendly Solutions: Deploy security tools that don't impede productivity
- Self-Service Capabilities: Enable employees to resolve common security issues independently
- Performance Optimization: Ensure security measures support rather than hinder remote work
Feedback and Communication
- Regular Surveys: Gather employee feedback about security challenges and solutions
- Open Channels: Maintain accessible communication paths for security questions and concerns
- Recognition Programs: Acknowledge employees who demonstrate excellent security practices
The Path Forward: Remote Work Security Maturity
Organizations must evolve their remote work security capabilities systematically:
Assessment and Gap Analysis
Current State Evaluation
- Comprehensive Security Assessment: Evaluate all aspects of remote work security
- Risk Prioritization: Identify and prioritize the most critical security gaps
- Resource Planning: Develop realistic timelines and budgets for security improvements
Benchmarking and Standards
- Industry Comparisons: Understand how your security posture compares to industry peers
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure remote work practices meet all applicable requirements
- Best Practice Adoption: Implement proven security frameworks and methodologies
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation (0-3 Months)
- Basic Controls: Implement fundamental security measures like VPN and MFA
- Policy Development: Establish clear remote work security policies and procedures
- Tool Deployment: Roll out essential security technologies to remote workers
Phase 2: Enhancement (3-12 Months)
- Advanced Capabilities: Deploy sophisticated threat detection and response tools
- Process Optimization: Refine security procedures based on operational experience
- Training Programs: Implement comprehensive security awareness initiatives
Phase 3: Optimization (12+ Months)
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly update security measures based on emerging threats
- Advanced Analytics: Leverage AI and machine learning for predictive security
- Strategic Integration: Align remote work security with broader business objectives
Measuring Remote Work Security Success
Key Performance Indicators
Security Metrics
- Incident Frequency: Track the number and severity of remote work security incidents
- Response Times: Measure how quickly security teams can respond to remote incidents
- Compliance Rates: Monitor adherence to remote work security policies and procedures
Business Impact Metrics
- Productivity Measures: Ensure security measures don't negatively impact employee productivity
- Employee Satisfaction: Track remote worker satisfaction with security tools and processes
- Cost Optimization: Measure the return on investment for remote work security initiatives
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Real-Time Visibility
- Dashboard Development: Create comprehensive views of remote work security posture
- Automated Alerting: Implement systems that notify security teams of potential issues
- Trend Analysis: Identify patterns and trends in remote work security data
Regular Reviews
- Quarterly Assessments: Conduct regular evaluations of remote work security effectiveness
- Threat Landscape Updates: Stay current with evolving threats targeting remote workers
- Technology Refreshes: Regularly evaluate and update remote work security technologies
Conclusion: Securing the Future of Work
The transition to remote and hybrid work models represents one of the most significant workplace transformations in modern history. Organizations that recognize remote work security as a strategic imperative—not just a compliance requirement—will be best positioned to thrive in this new environment.
Success requires more than technology deployment. It demands cultural transformation, strategic investment, and ongoing commitment to security excellence. The organizations that master remote work security will not only protect their assets and reputation but also attract top talent who value flexible work arrangements supported by robust security measures.
The future belongs to organizations that can seamlessly blend productivity, flexibility, and security. The question isn't whether remote work will continue—it's whether your organization will be prepared to secure it effectively.
Ready to evaluate your remote work security posture? Take our comprehensive 10-minute assessment to receive a detailed security score and personalized recommendations for improving your organization's distributed workforce security.