Azure Security Technical Brief for CISOs

Comprehensive Guide to Azure Security Strategy and Implementation
Executive Summary
Microsoft Azure has undergone significant security transformations in 2025, driven by the Secure Future Initiative (SFI) and enhanced Zero Trust architecture. This brief provides CISOs with strategic insights into Azure's current security capabilities, compliance frameworks, and implementation best practices for enterprise-grade cloud security.
Key Takeaways:
- Azure's Secure Future Initiative represents the largest cybersecurity engineering project in Microsoft's history
- Zero Trust architecture is now deeply integrated across all Azure services
- AI-powered security capabilities provide real-time threat detection and response
- Comprehensive compliance coverage spans 100+ regulatory frameworks globally

1. Strategic Security Framework
Microsoft Secure Future Initiative (SFI)
Microsoft launched SFI in late 2023 as a multi-year commitment involving 34,000 engineers across 14 product divisions. The initiative has delivered:
- Enhanced Identity Protection: Entra ID and Microsoft Account token signing keys now secured in hardware-based security modules (HSMs)
- Improved Detection Capabilities: 200+ additional threat detections integrated into Microsoft Defender
- Cultural Transformation: Security-first culture embedded across all engineering teams
- Executive Accountability: Executive compensation directly tied to security performance metrics
Zero Trust Implementation at Scale
Azure's Zero Trust approach operates on three core principles:
- Verify Explicitly: Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points
- Use Least Privileged Access: Implement just-in-time (JIT) and just-enough-access (JEA)
- Assume Breach: Minimize blast radius through network segmentation and continuous monitoring
Key Zero Trust Components:
- Conditional Access: Primary policy engine for Zero Trust architecture
- Passwordless Authentication: FIDO2 security keys and biometric authentication
- Microsegmentation: Isolation of Azure workloads into security zones
- Continuous Trust Scoring: AI-powered risk assessments for authentication workflows

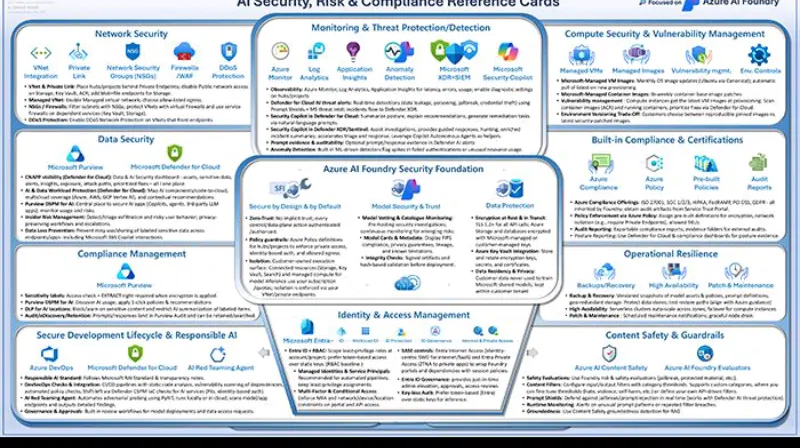
2. Core Security Architecture
Identity and Access Management
Azure Active Directory (Entra ID) provides comprehensive identity governance:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Mandatory for privileged accounts
- Privileged Identity Management (PIM): Just-in-time access for administrative roles
- Conditional Access Policies: Risk-based access controls
- Identity Protection: AI-driven threat detection for identity risks
Network Security Services
Defense-in-Depth Network Protection:
- Azure Firewall: Next-generation firewall with threat intelligence
- Network Security Groups (NSGs): Host-level traffic filtering
- Azure DDoS Protection: Comprehensive DDoS mitigation
- Azure Bastion: Secure RDP/SSH connectivity without public IPs
- Private Link: Network-level isolation for PaaS services
Data Protection
Comprehensive Data Security Controls:
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE): Encryption at rest for databases
- Always Encrypted: Client-side encryption for sensitive data
- Azure Key Vault: Centralized key management with HSM support
- Microsoft Purview: Data governance and classification
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Automated sensitive data protection
3. AI Security and Governance
Azure AI Security Framework
With AI adoption accelerating, Azure provides specialized security for AI workloads:
Azure AI Foundry Security Features:
- Model Scanning: Pre-deployment security testing for AI models
- Prompt Injection Protection: Real-time detection of malicious prompts
- Data Boundary Enforcement: Strict separation of training and inference data
- Confidential Computing: AI workloads in encrypted environments
AI Governance and Compliance
Entra Agent ID: Centralized identity management for AI agents and human users Microsoft Purview SDK: Policy enforcement and auditing for AI systems Compliance Workflows: Integration with regulatory frameworks for AI governance
AI-Specific Risk Management
- MITRE ATLAS Framework: Structured approach to AI security threats
- OWASP Generative AI Risk: Best practices for generative AI security
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time detection of AI model drift and anomalies

4. Compliance and Regulatory Framework
Global Compliance Coverage
Azure maintains certification across 100+ compliance frameworks:
Healthcare:
- HIPAA/HITECH (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
- HITRUST (Health Information Trust Alliance)
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
Financial Services:
- SOC 1, 2, 3 (Service Organization Control)
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- ISO 27001/27017/27018
Government:
- FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program)
- DoD IL2-IL6 (Department of Defense Impact Levels)
- CJIS (Criminal Justice Information Services)
Compliance Automation Tools
Azure Policy: Automated compliance enforcement across resources Microsoft Purview Compliance Manager: Centralized compliance assessment and tracking Azure Blueprints: Pre-configured compliance templates for rapid deployment

5. Operational Security Best Practices
Security Operations Center (SOC) Integration
Microsoft Sentinel provides cloud-native SIEM capabilities:
- AI-Powered Analytics: Machine learning for threat detection
- Automated Response: Playbooks for incident response
- Threat Intelligence: Global threat data integration
- Custom Detection Rules: Tailored security monitoring
Vulnerability Management
Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers comprehensive security posture management:
- Continuous Assessment: Real-time vulnerability scanning
- Secure Score: Quantified security posture measurement
- Regulatory Compliance Dashboard: Compliance status tracking
- Workload Protection: Runtime protection for VMs, containers, and databases
Incident Response Framework
Structured Incident Response Process:
- Detection: Automated threat detection and alerting
- Investigation: AI-assisted threat hunting and analysis
- Containment: Automated isolation and remediation
- Recovery: Validated restoration procedures
- Lessons Learned: Continuous improvement integration
6. Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-3)
Identity Security:
- Deploy Azure Active Directory with MFA
- Implement Privileged Identity Management
- Configure Conditional Access policies
- Enable Identity Protection
Network Security:
- Deploy Azure Firewall and NSGs
- Implement network segmentation
- Configure DDoS protection
- Establish secure connectivity (VPN/ExpressRoute)
Phase 2: Advanced Protection (Months 4-6)
Data Protection:
- Deploy Azure Key Vault with HSM
- Implement data classification with Purview
- Configure encryption at rest and in transit
- Establish data loss prevention policies
Monitoring and Response:
- Deploy Microsoft Sentinel
- Configure automated response playbooks
- Implement threat hunting capabilities
- Establish SOC procedures
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 7-12)
AI Security Integration:
- Deploy AI workload protection
- Implement AI governance framework
- Configure AI-specific monitoring
- Establish AI risk management procedures
Compliance and Governance:
- Implement regulatory compliance frameworks
- Automate compliance reporting
- Conduct regular security assessments
- Optimize security policies based on metrics
7. Cost Optimization and ROI
Security Investment Prioritization
High-Impact, Low-Cost Initiatives:
- Multi-factor authentication deployment
- Basic network segmentation
- Automated patch management
- Security awareness training
Medium-Term Investments:
- Advanced threat protection
- Security information and event management (SIEM)
- Data loss prevention solutions
- Compliance automation tools
Strategic Long-Term Investments:
- Zero Trust architecture implementation
- AI-powered security operations
- Advanced persistent threat (APT) protection
- Quantum-resistant cryptography preparation
Shared Responsibility Model Benefits
Azure-Managed Security Controls:
- Physical datacenter security
- Infrastructure patching and maintenance
- Network infrastructure protection
- Hardware security module management
Customer-Managed Security Controls:
- Identity and access management
- Application-level security
- Data classification and protection
- Security monitoring and response
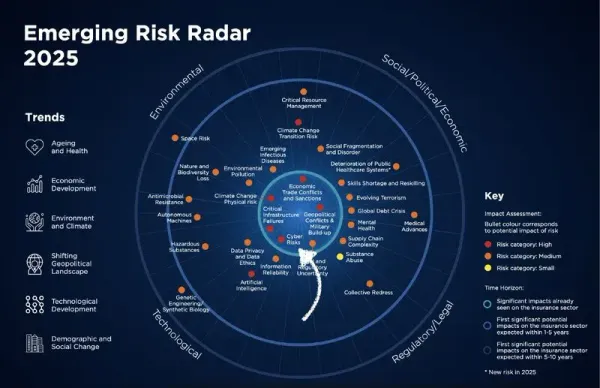
8. Emerging Threats and Future Considerations
Quantum Computing Preparedness
Post-Quantum Cryptography:
- Azure Key Vault quantum-resistant algorithm support
- Migration planning for quantum-safe encryption
- Timeline alignment with NIST standards
- Risk assessment for current cryptographic implementations
AI-Powered Threat Landscape
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs):
- AI-enhanced social engineering attacks
- Machine learning model poisoning
- Automated vulnerability exploitation
- Deepfake and synthetic media threats
Regulatory Evolution
Emerging Compliance Requirements:
- EU AI Act implementation
- Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)
- State-level privacy regulations
- Supply chain security mandates

9. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Security Metrics Dashboard
Technical Metrics:
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD): Target <15 minutes
- Mean Time to Response (MTTR): Target <1 hour
- Secure Score: Target >80%
- Critical vulnerabilities: Target 0 open >30 days
Operational Metrics:
- Security incident frequency: Monthly trend analysis
- Compliance audit results: 100% pass rate target
- Employee security training completion: 95% target
- Security awareness phishing simulation results
Business Metrics:
- Security-related downtime: Target <0.1%
- Data breach incidents: Target 0
- Compliance violation costs: $0 target
- Security ROI measurement: Annual assessment
10. Recommended Actions
Immediate (Next 30 Days)
- Conduct Azure Security Assessment: Evaluate current security posture using Azure Secure Score
- Implement MFA: Deploy multi-factor authentication for all privileged accounts
- Enable Basic Monitoring: Activate Azure Monitor and basic alerting
- Review Access Permissions: Audit and remediate excessive privileges
Short-Term (Next 90 Days)
- Deploy Zero Trust Framework: Implement Conditional Access policies
- Enhance Network Security: Configure Azure Firewall and network segmentation
- Establish SIEM Capability: Deploy Microsoft Sentinel for security monitoring
- Implement Data Protection: Configure encryption and data classification
Long-Term (6-12 Months)
- AI Security Integration: Deploy AI workload protection and governance
- Advanced Threat Protection: Implement comprehensive EDR/XDR capabilities
- Compliance Automation: Automate regulatory compliance monitoring
- Quantum Readiness: Begin transition to post-quantum cryptography
Conclusion
Azure's comprehensive security framework provides enterprise-grade protection through integrated identity management, network security, data protection, and AI-powered threat detection. The combination of Microsoft's Secure Future Initiative, Zero Trust architecture, and extensive compliance coverage positions Azure as a strategic platform for secure cloud transformation.
CISOs should prioritize identity security as the foundation, implement network segmentation for defense-in-depth, and leverage AI-powered security operations for scalable threat detection and response. The shared responsibility model allows organizations to benefit from Microsoft's security expertise while maintaining control over application and data security.
Success requires a phased implementation approach, continuous monitoring and optimization, and alignment with business objectives. By following the recommended roadmap and best practices outlined in this brief, organizations can achieve a robust, compliant, and cost-effective cloud security posture.
This brief is based on Microsoft Azure security capabilities as of August 2025. Organizations should consult with Azure security specialists and conduct thorough assessments before implementation.