AI-Powered Cybersecurity: The Key to Saudi Arabia's Growing Cyber Defense Efforts

As the digital world becomes increasingly interconnected, the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks are on the rise. In response, countries like Saudi Arabia are turning to artificial intelligence (AI) to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. In 2023 alone, Saudi Arabia’s cybersecurity spending reached a remarkable $3.55 billion, a 10.83% increase from the previous year, demonstrating its commitment to staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.

AI: The Game Changer in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence has become a game-changer in the fight against cyberattacks. Traditional cybersecurity measures, while effective, often struggle to keep pace with the ever-evolving tactics used by hackers. This is where AI steps in, providing enhanced automation, real-time threat detection, and predictive capabilities that allow security systems to sift through vast datasets and flag suspicious activities in real time. This proactive defense is critical in today’s world, where cyber threats—ranging from phishing to ransomware—are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
Moataz BinAli, regional vice president and managing director for the Mediterranean, Middle East, and Africa region at Trend Micro, explained that AI-powered tools not only detect but also learn from past cyberattacks, enabling them to adapt to new tactics used by hackers. “AI-powered tools can help organizations stay ahead by learning from previous cyberattacks and continuously adapting to new tactics used by hackers,” said BinAli.
Saudi Arabia's Cybersecurity Leadership
In 2024, Saudi Arabia achieved a significant milestone by securing the top spot in the UN Global Cybersecurity Index, receiving a perfect score across five key pillars: legal, organizational, cooperation, capacity development, and technical measures. This achievement underscores the Kingdom’s commitment to building a resilient cybersecurity infrastructure, both in the public and private sectors.
The Kingdom’s substantial investments in cybersecurity align with its broader Vision 2030 goals, which focus on economic diversification and technological advancement. By integrating AI-driven technologies into its cybersecurity strategy, Saudi Arabia has positioned itself as a global leader in cyber defense, setting a high standard for other nations to follow.
AI-Powered Tools for Real-Time Threat Detection
One of the most valuable aspects of AI in cybersecurity is its ability to detect threats in real time. AI-powered solutions can automatically analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and flag anomalies that might indicate a cyberattack. In environments where speed and accuracy are critical, such as banking or critical infrastructure, AI enables rapid response to emerging threats.
For example, Trend Micro has developed AI-powered solutions like its flagship platform Trend Vision One, which provides extended detection and response (XDR) across various environments, including endpoints, emails, networks, and servers. This unified approach allows for real-time threat monitoring and proactive response to potential cyber threats. Additionally, Trend Micro’s Attack Surface Risk Management tool helps organizations assess and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
A Multi-Layered Approach to Cybersecurity
Despite the power of AI, cybersecurity experts emphasize that technology alone is not enough to fend off cyberattacks. A multi-layered approach is required, combining AI with human expertise and basic cybersecurity practices. Moataz BinAli highlighted that enforcing strong password policies, using multi-factor authentication (MFA), and conducting regular software updates are essential steps in creating a robust cybersecurity framework.
Human error remains one of the weakest links in cybersecurity, often exploited through phishing and social engineering tactics. To address this, employee training and awareness programs are critical. Continuous education helps employees recognize and avoid phishing scams, reducing the risk of successful cyberattacks.
Challenges and Opportunities in AI-Driven Cybersecurity
While AI offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges. Cybercriminals are increasingly weaponizing AI to automate phishing campaigns, develop adaptive malware, and bypass traditional security defenses. The same technologies that bolster cybersecurity can also be used by hackers to enhance their attacks.
Another challenge lies in the false positives generated by AI systems. According to Trend Micro’s Attack Surface Risk Management data, more than 40% of companies using AI in their cybersecurity report excessive false alerts. These false positives can overwhelm security teams, diverting their attention from actual threats and complicating incident response efforts.
However, AI’s potential in cybersecurity far outweighs its challenges. By continuing to improve data quality and refining algorithms, organizations can minimize false positives and enhance the accuracy of their AI-driven defenses.
The Future of AI in Cybersecurity
As Saudi Arabia continues to invest in cutting-edge technologies, AI will remain at the forefront of its cybersecurity strategy. With the global threat landscape constantly evolving, the Kingdom’s ability to integrate advanced AI solutions into its digital infrastructure will be crucial in maintaining its leadership in the global cybersecurity arena.
By focusing on real-time threat detection, adaptive security measures, and a multi-layered defense strategy, Saudi Arabia is setting a new standard for cybersecurity. As the Kingdom’s investments in AI and cybersecurity grow, it will serve as a model for other nations striving to protect their digital assets and critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
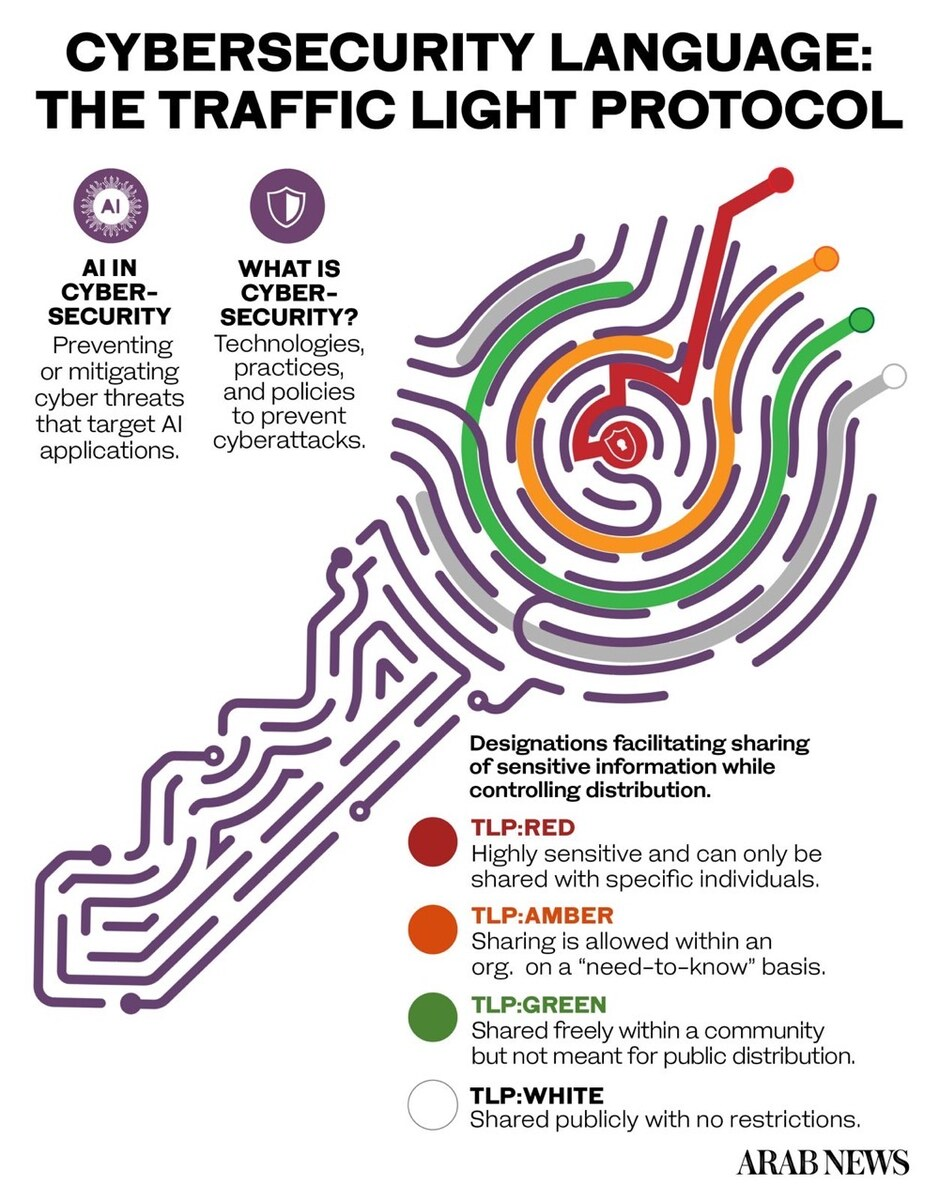
Traffic Light Protocol (TLP):
- The TLP is a widely used method to categorize and share sensitive information securely.
- TLP: RED is the most restricted, meant for specific individuals.
- TLP: AMBER allows sharing within an organization on a need-to-know basis.
- TLP: GREEN is shared freely within a community but not for public distribution.
- TLP: WHITE can be shared publicly with no restrictions.





